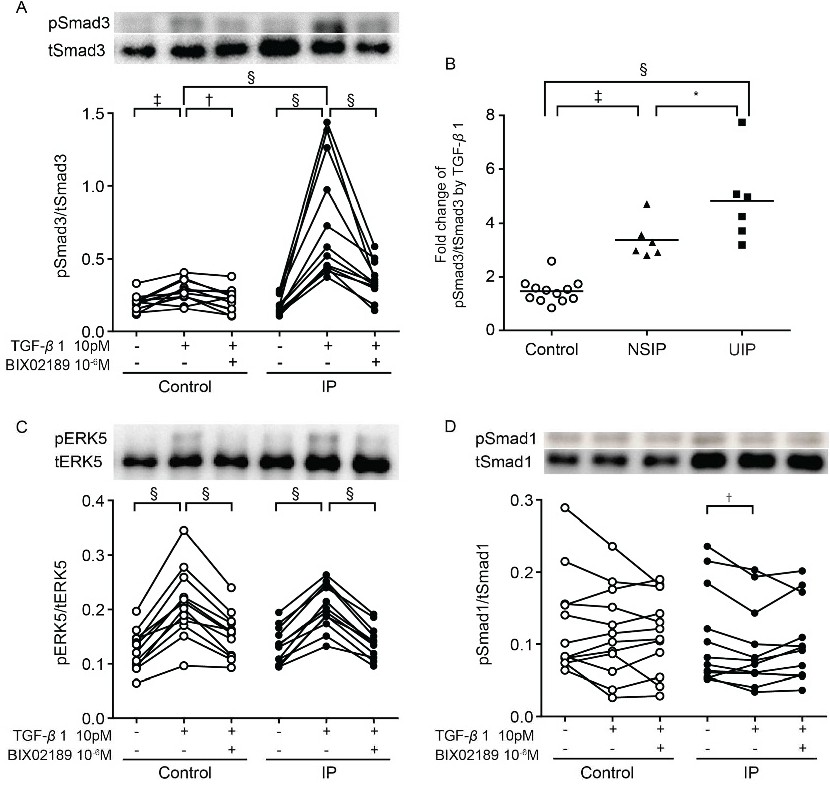
Fig. 5. Regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 signaling in lung fibroblasts from control and lung fibrotic (interstitial pneumonia, IP) subjects. (A, C, D) Effect of BIX02189 on TGF-β1-induced Smad3 (A), extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK)5 (C), and Smad1 (D) phosphorylation. Sub-confluent fibroblasts were cultured in serum-free (SF)-DMEM for 24 h and then incubated in the presence or absence of TGF-β1 or BIX02189 for 8 h. Total protein was extracted, and western blotting was performed with specific antibodies against phospho-Smad3 (pSmad3), Smad3 (tSmad3), ERK5 (tERK5), phospho-Smad1 (pSmad1), and Smad1 (tSmad1). Phospho-ERK5 (pERK5) can be detected as a band with slower electrical migration that represents the active form of the protein [1]. The vertical axes show the relative ratio of phospho-Smad3 to total Smad3, phospho-ERK5 to total ERK5, or phospho-Smad1 to total Smad1; the horizontal axes show the conditions. (B) Relative increases in Smad3 phosphorylation in the control, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, and usual interstitial pneumonia groups after TGF-β1 stimulation. The vertical axis shows the ratio of fold increase in phospho-Smad3 to total Smad3. The values represent mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *P<0.05, †P<0.01 ‡P<0.005, §P<0.001 (A-D).